This article is a technical analysis of a project code submitted as part of an entry in the Zindi "Digital Africa Plantation Counting Challenge" [1]. The challenge aimed to develop a machine learning algorithm capable of accurately detecting and counting the number of palm oil trees in aerial images captured from drones. The code for the approach described here is available on Github [2].
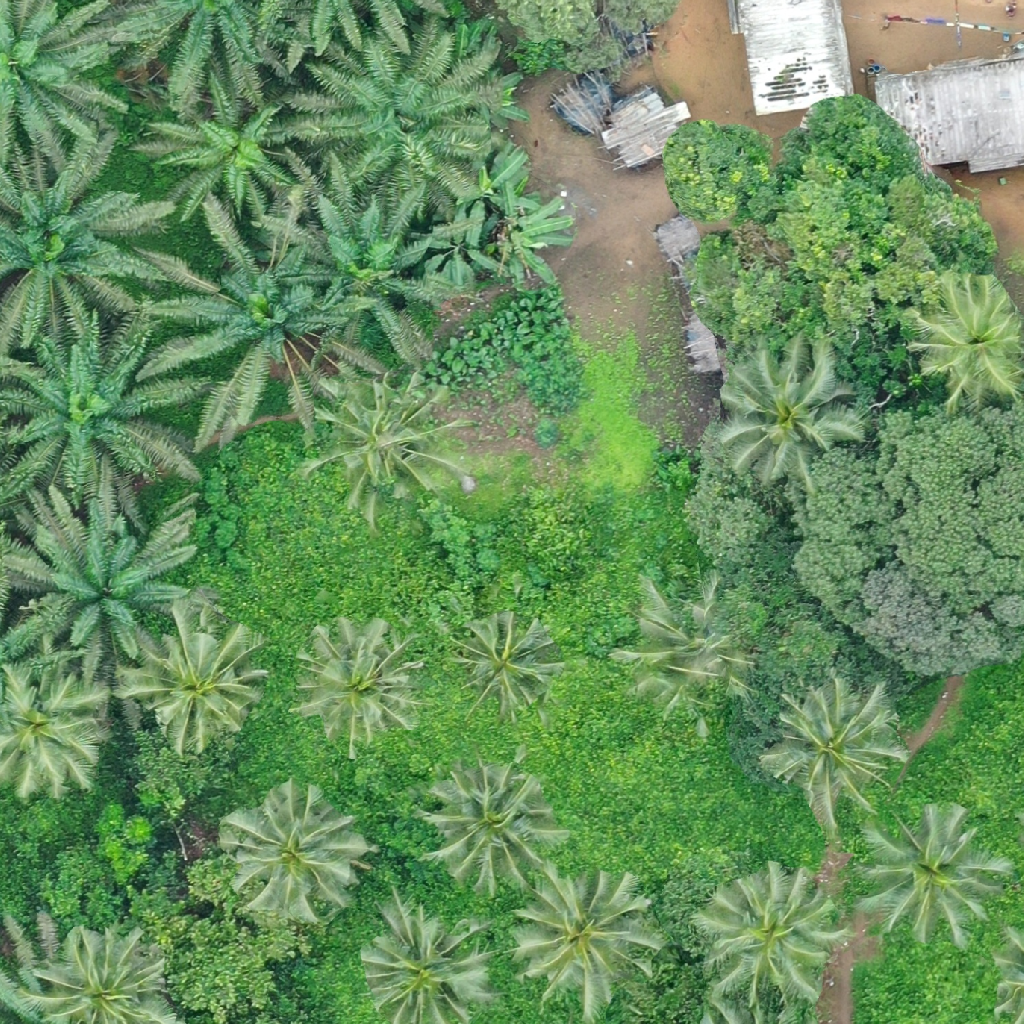

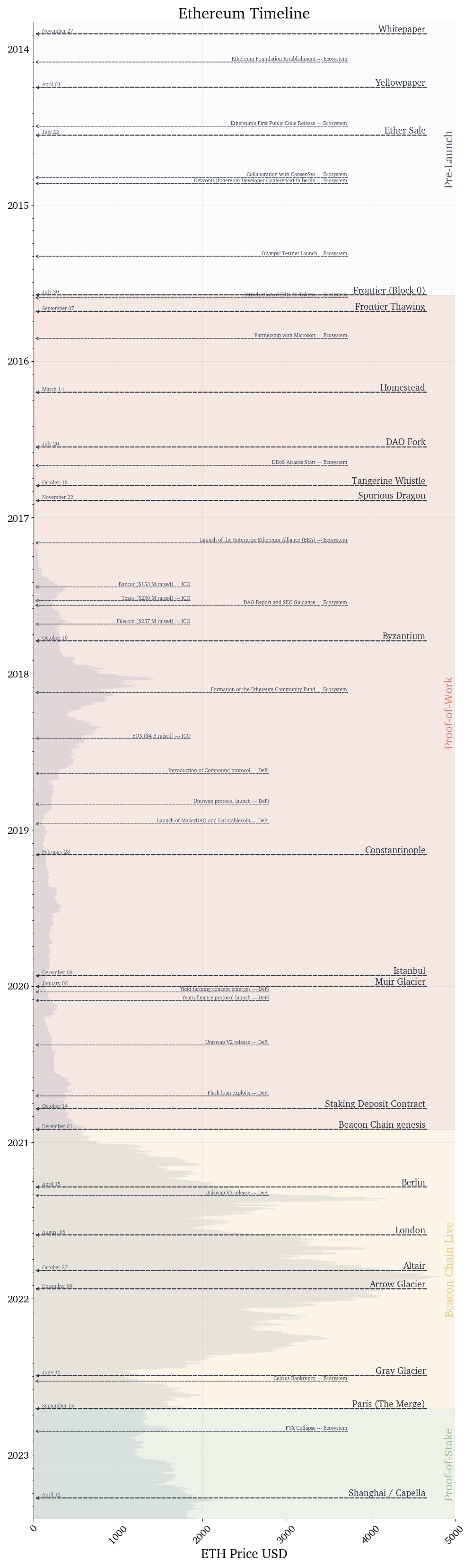
Electronic ink (e-ink) displays are composed of an array of tiny micro-capsules embedded in a layer between two electrodes. Each micro-capsule in the array contains both positively charged white particles, and negatively charged black particles. These particles are suspended in a transparent oil. When a voltage is applied across the micro-capsule, the black and white particles separate. With either the black particles or white particles moving to the top of the micro-capsule, creating a white or black dot depending on the charge [1].
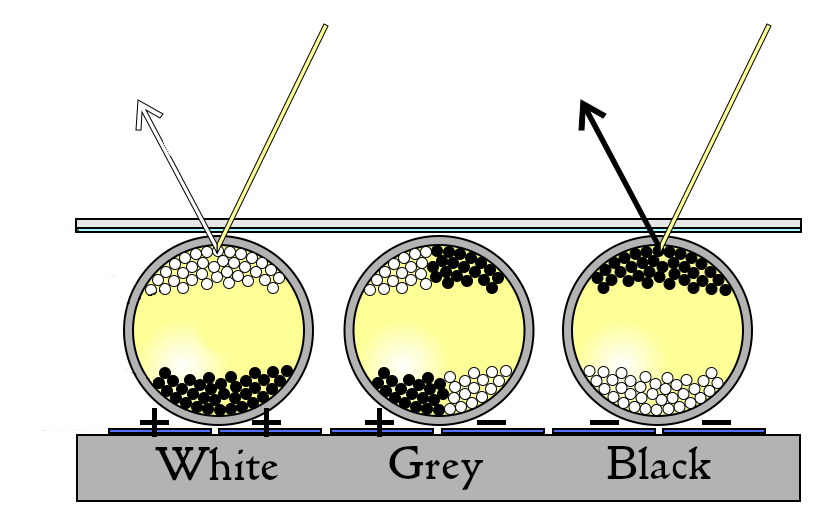
This is a short guide on creating custom scheduled Linux desktop notifications with anacron and notify-send. This system could be used to set reminders for tasks you intend to complete @daily, @weekly, @monthly, or @yearly, and can also display metrics you are interested to follow.
The Unix operating system is a multitasking, multiuser operating system that started life under the initiative of Ken Thompson in the late 1960s at AT&T Bell Labs in New Jersey, United States. Researchers at Bell Labs are also credited with developing radio astronomy, the transistor, the laser, the photovoltaic cell, the charge-coupled device (CCD), information theory, and the programming languages B, C, C++, S, SNOBOL, AWK, AMP [1]. Unix has become widely used in many computing systems, including desktop computers, servers, laptops, and mobile devices.
Linux is a UNIX-like clone that was developed independently starting in 1991 by Linus Torvalds and team. The Linux kernel was designed in such a way so that it acts like Unix but from a different code base. This Linux kernel is generally packaged within Linux distributions to form a complete operating system. Unix and Unix-like systems form the backbone of many modern software services due to their robustness, portability, and flexibility. They also have extensive software libraries and features like a hierarchical file system and unified directory structure.
A shell or command-line interpreter (CLI) provides an interface for a user to input commands in Unix-like operating systems. The shell can be used as an interactive command prompt and also written as a scripting programming language. Typically users interact with the shell using a text window called a terminal emulator, that is a computer program that emulates a video terminal. The shell maybe executing directly on the local hardware or remotely connecting to a server via Secure Shell (SSH). All Unix shells provide filename wildcarding, piping, here documents, command substitution, variables and control structures for condition-testing and iteration [1].
The Bourne Again SHell (bash) is the Unix-shell and command language for the GNU operating system written by Brian Fox and first released in 1989. It serves as a replacement to its predecessor the Bourne Shell (sh), and has a superset of its features. The bash shell incorporates features from the Bourne shell (sh) the KornShell (ksh) and the C shell (csh). For example the expansion of the tilde ~ character to the value held in the $HOME environment variable comes from the C shell. Bash has gone on to become the most popular shell among users of Linux and the default on many distributions [2].
Some Notes on Python language features, with examples...
Motivation: here I provide some notes made whilst reviewing the book "Python tricks" by Dan Bader, which is a very useful highly recommended book available here. Python has become the third most popular programming language behind Java and C, and it continues to become more popular. It is an easy to learn high-level language, that is fun to use and learn. Some of the more advanced and interesting language features are discussed here.
Bitcoin is open-source; its design is public, nobody owns or controls Bitcoin and everyone can take part. - bitcoin.org
Background: the Bitcoin white paper was released under the pseudo-name Satoshi Nakamoto on 2008-10-31, poignantly this was a time when the traditional banking system was in turmoil at the onset of a global financial crisis. The identity of Author Satoshi Nakamoto is not known, with some speculating that Satoshi is actually a group rather than an individual. Satoshi circulated the Bitcoin paper on an internet mailing list for Cypherpunks, a group of activists that advocate the use of cryptography and privacy enhancing technologies as a route to social and political change. Creating a digital money independent of the traditional banking system for use on the internet had been a long term aspiration of the libertarian minded Cypherpunks. Ironically, much of the cryptography underpinning the sometimes lofty idealism of the Cypherpunk movement was developed in the 1970s within government intelligence agencies the NSA (USA) and GCHQ (UK).
Described here is an approach to the 2018 Data Science Bowl competition, this soluction scored within the top 20% of submissions, out of over 3000 teams. The objective of the competition was to segment nuclei in cell microscopy images.
Identifying cell nuclei is the starting point for many biological analyses. Most of the human body’s 30 trillion cells contain a nucleus full of DNA, the genetic code that programs each cell. Segmenting nuclei allows researchers to identify individual cells in a sample, measure their morphometry, and analyse how cells react to drug treatments.
This proof-of-concept system assess vessels in a risk framework considering multiple factors to suggest the likelihood that a vessel has been engaging in illegal, unregulated, or unreported (IUU) fishing. The framework combines automatic identification system (AIS) tracking data with satellite imagery in construction of a risk framework. The framework combines several indicators including: the likelihood that a vessel has previously fished in a marine protected area (MPA) or exclusive economic zone (EEZ), and the intermittency of the vessel's AIS signal.
Vessel risk indicators may be considered individually, or weighted according to the users interest, or combined into a unified vessel risk score. This information is displayed in a front end web application, which gives governments, NGOs, retailers, and enforcement agencies the information to distinguish responsible and legitimate vessels from vessels engaging in IUU fishing. For example, this could be used by retailers to check the risk score of vessels that supply their tuna, or to guide enforcement agencies in choosing which areas to patrol.